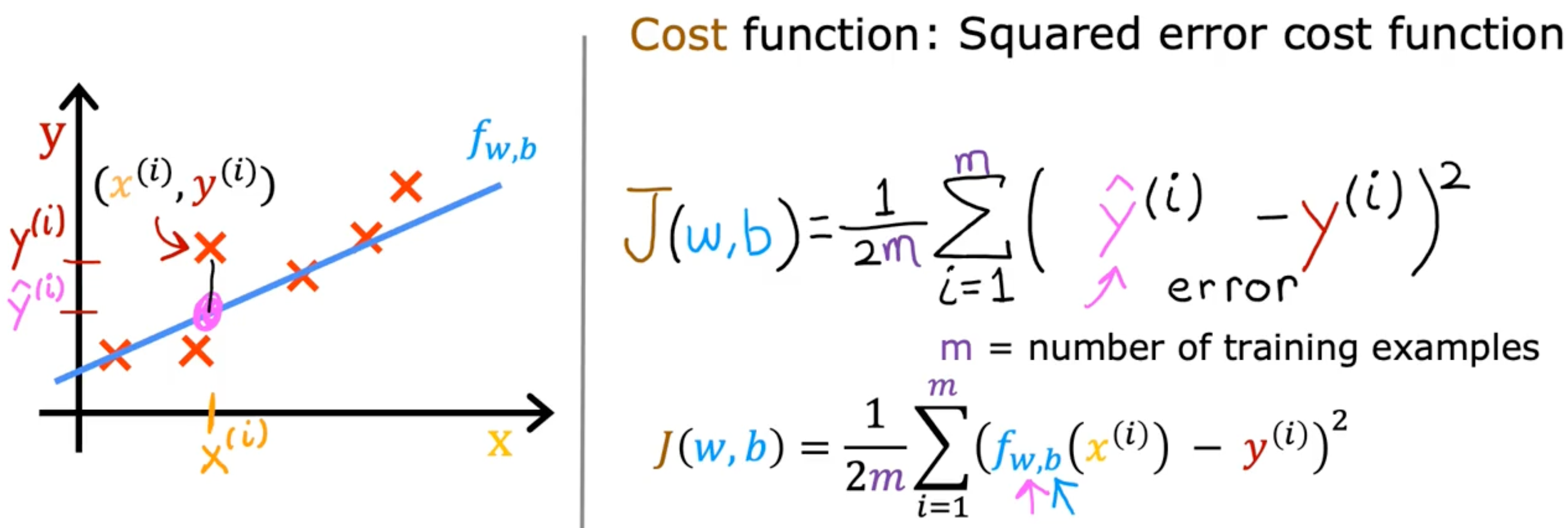1. Introduction to machine learning
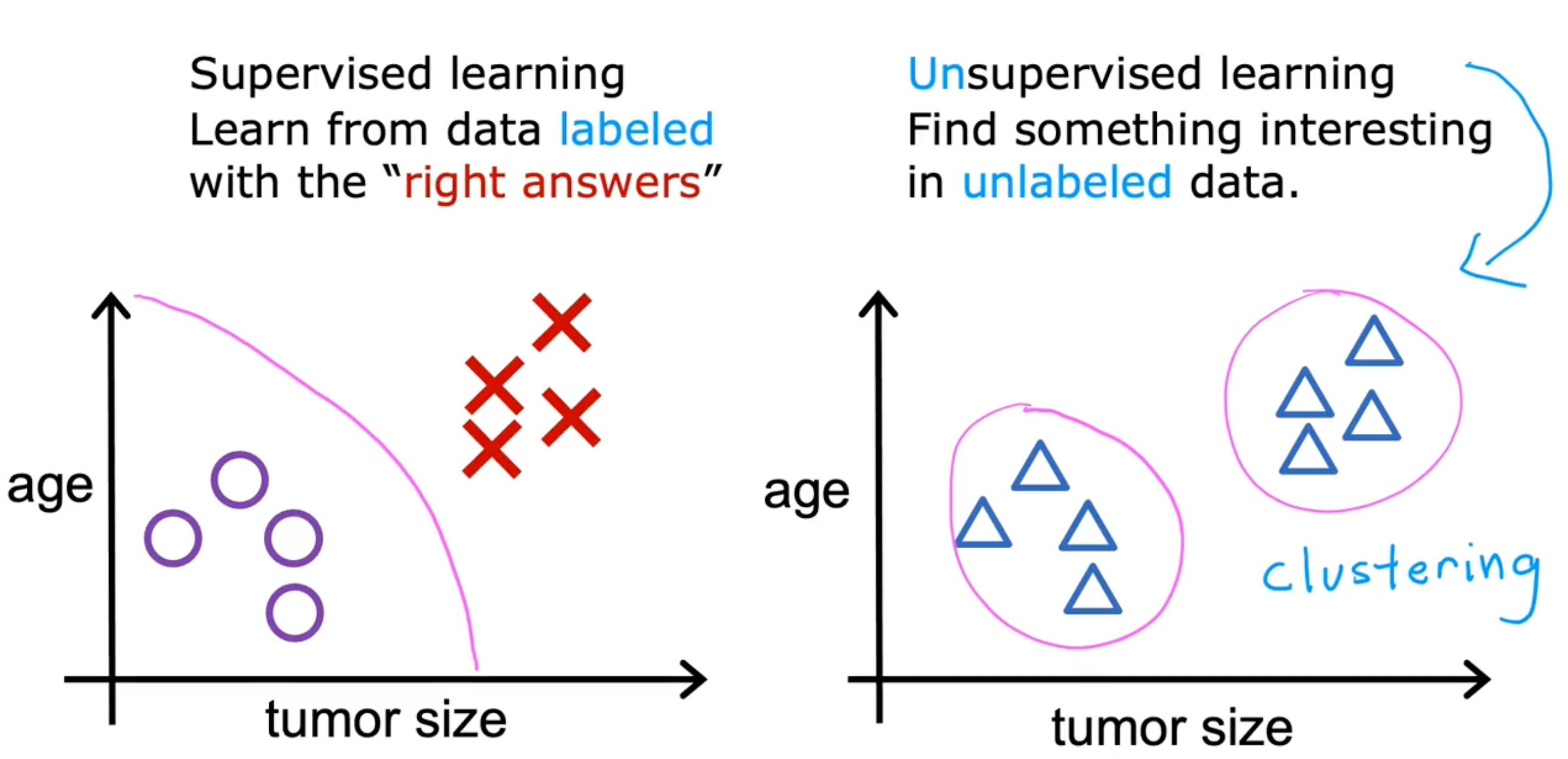
Supervised learning
input x → output y (learns from being right answers)
- Examples
- Spam email filtering
- Audio text transcripts (speech recognition)
- Language translations
- Online advertisement
- Self-driving car
- Visual inspection
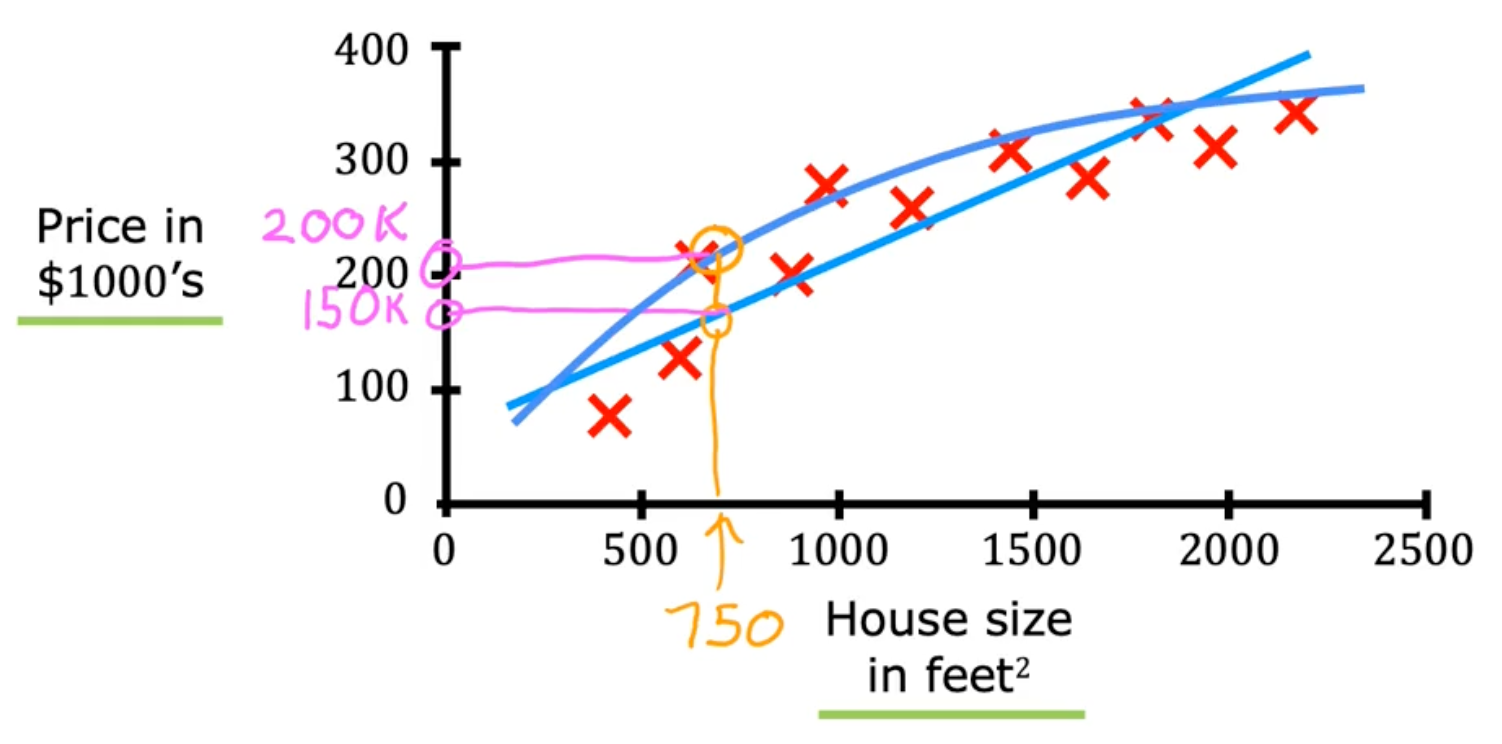
Regression
Regression predicts a number infinitely many possible outputs
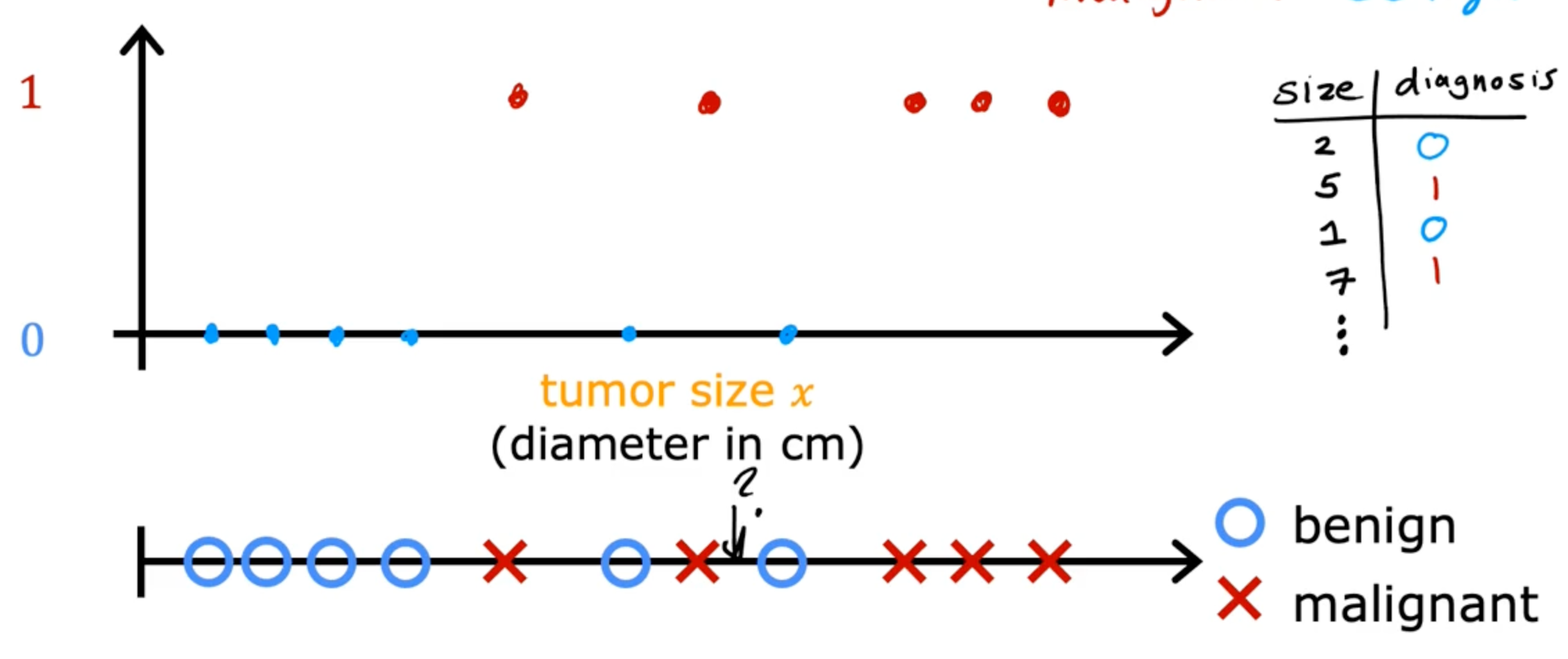
Classification
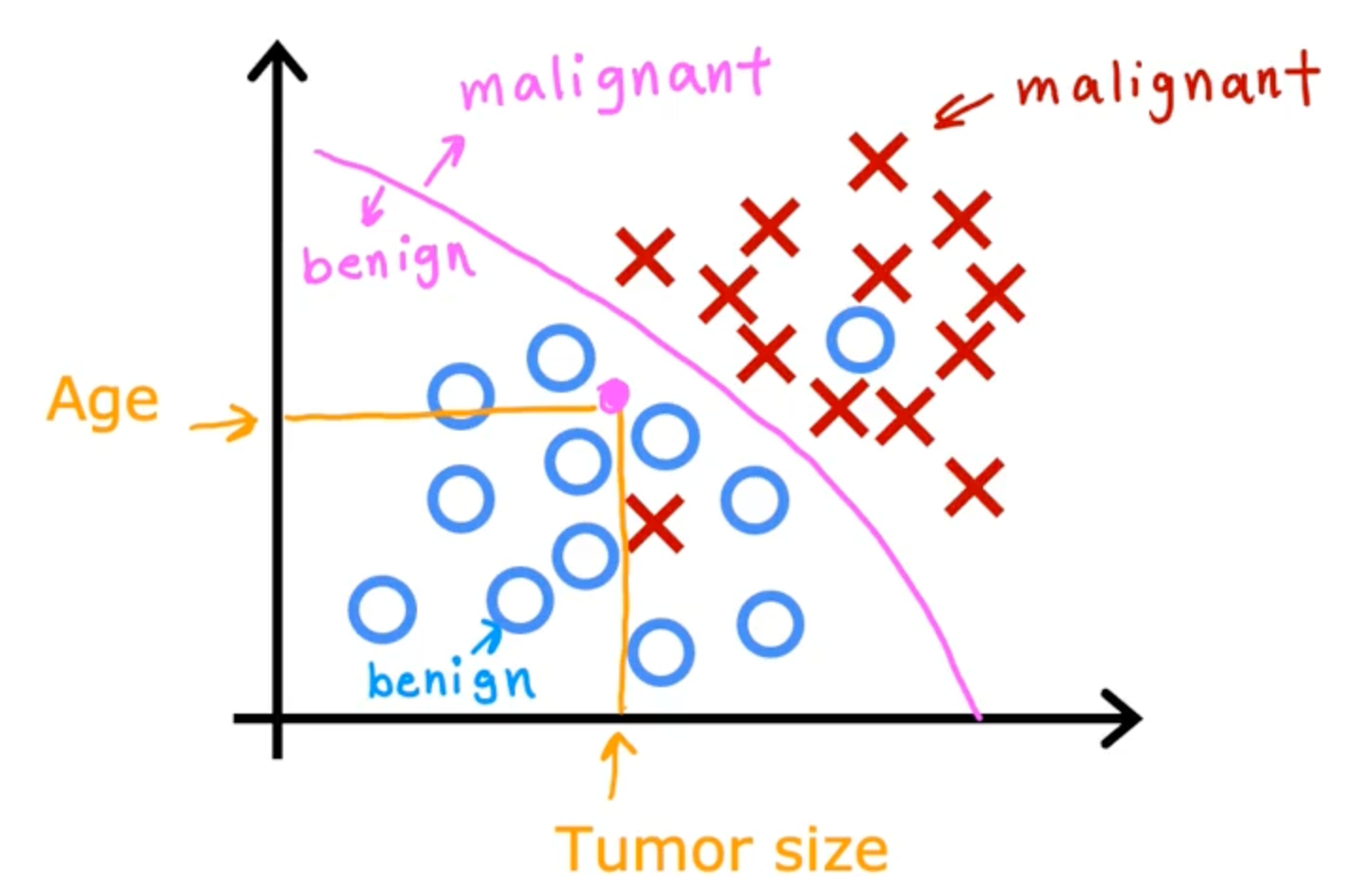
Classification predicts categories, small number of possible outputs
Unsupervised Learning
Find something interesting in unlabeled data
- example
-
Google news
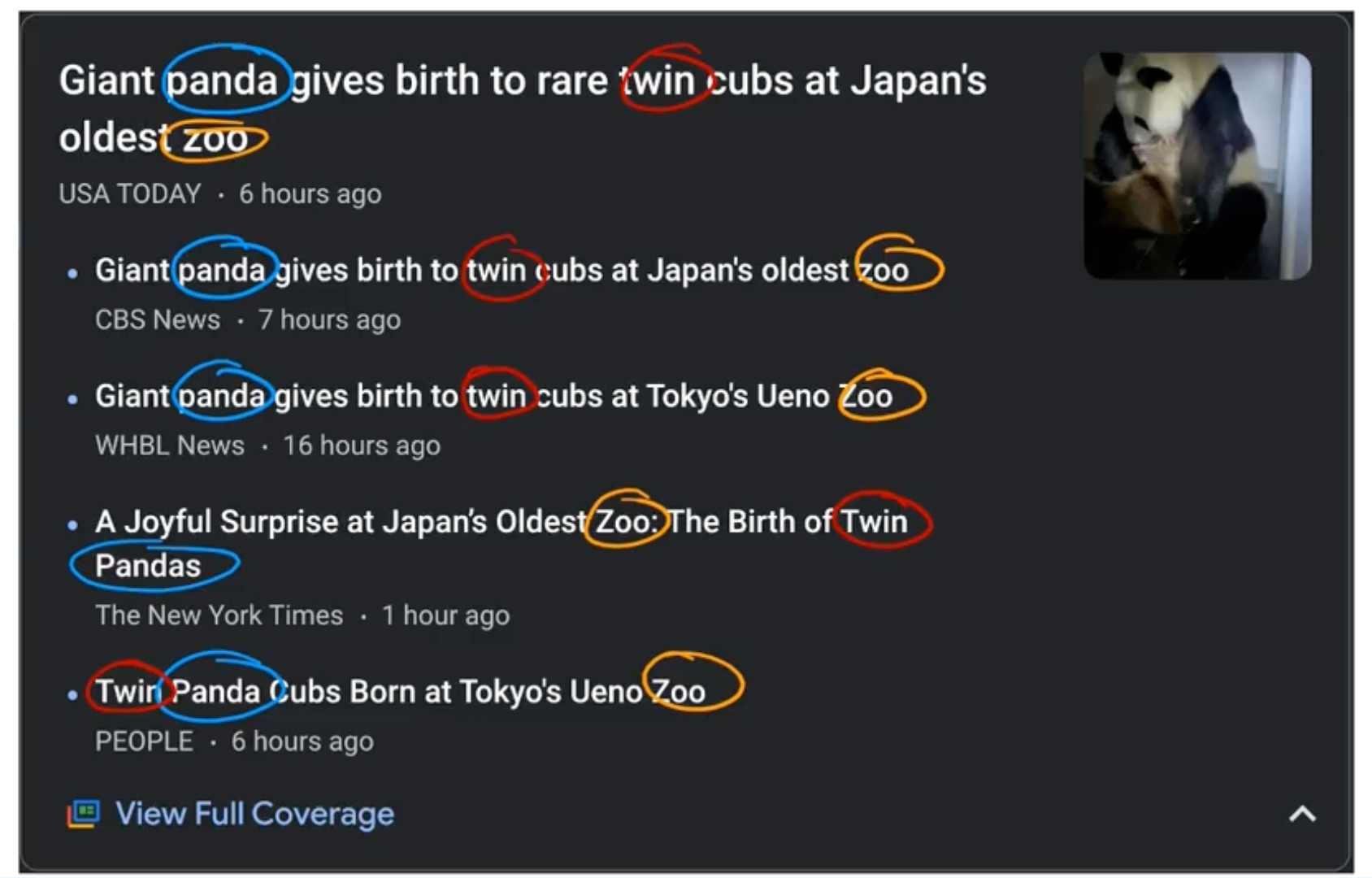
-
DNA microarray
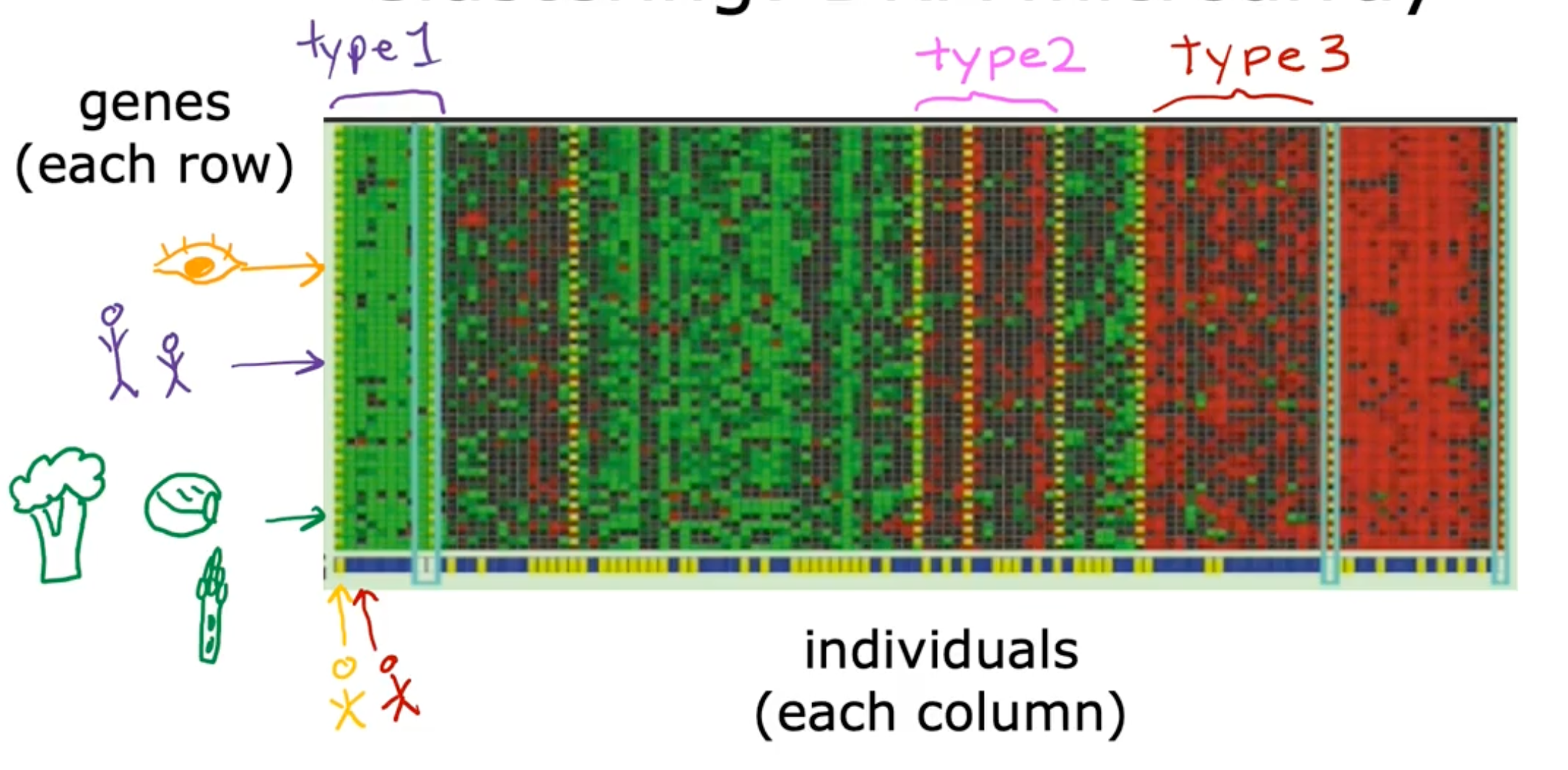
Unsupervised learning
Data only comes with inputs x, but not output labels y: Algorithm has to find structure in the data
- clustering - group similar data points together
- Anomaly detection - find unusual data points
- Dimensionality reduction - compress data using fewer numbers
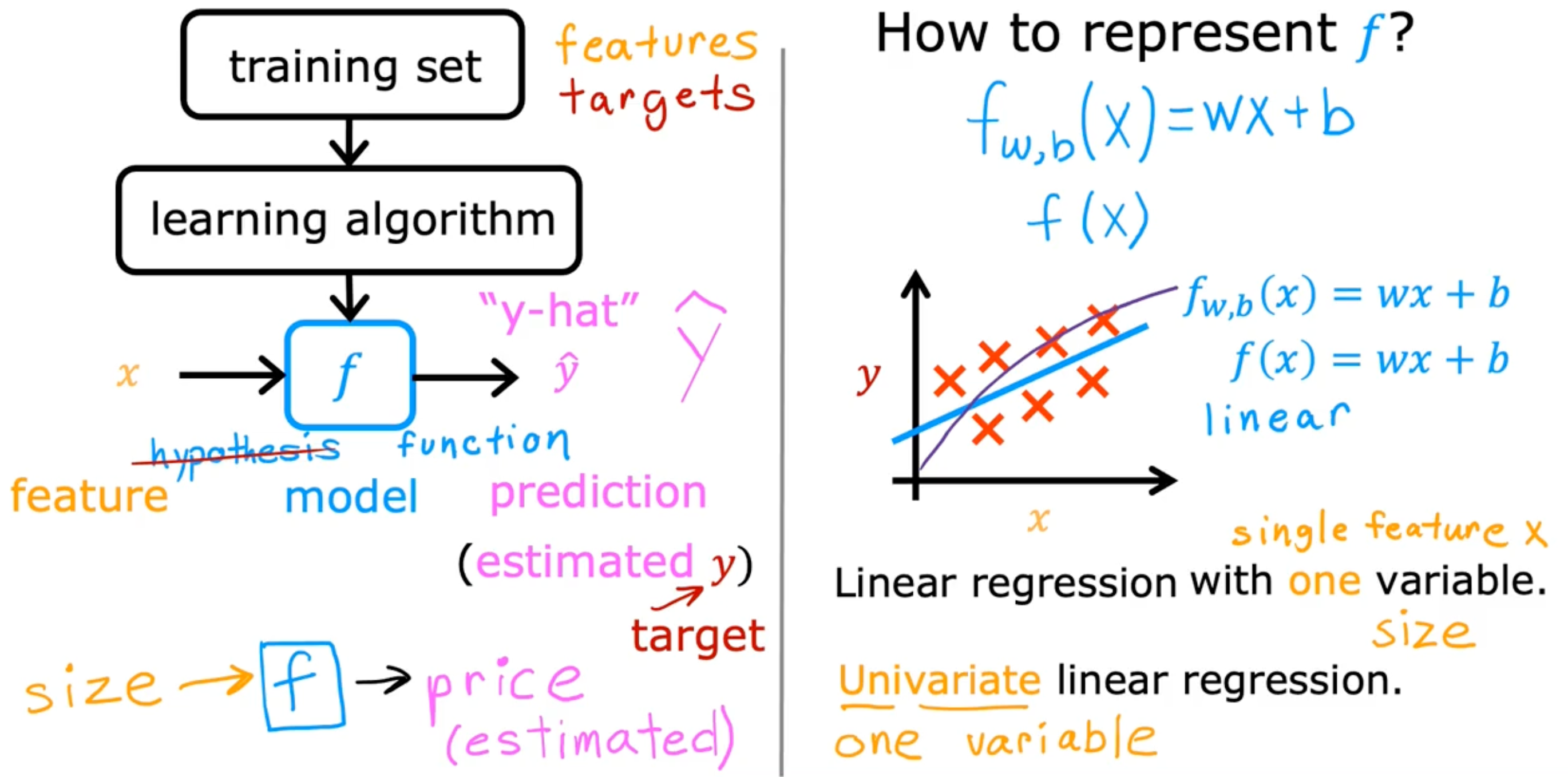
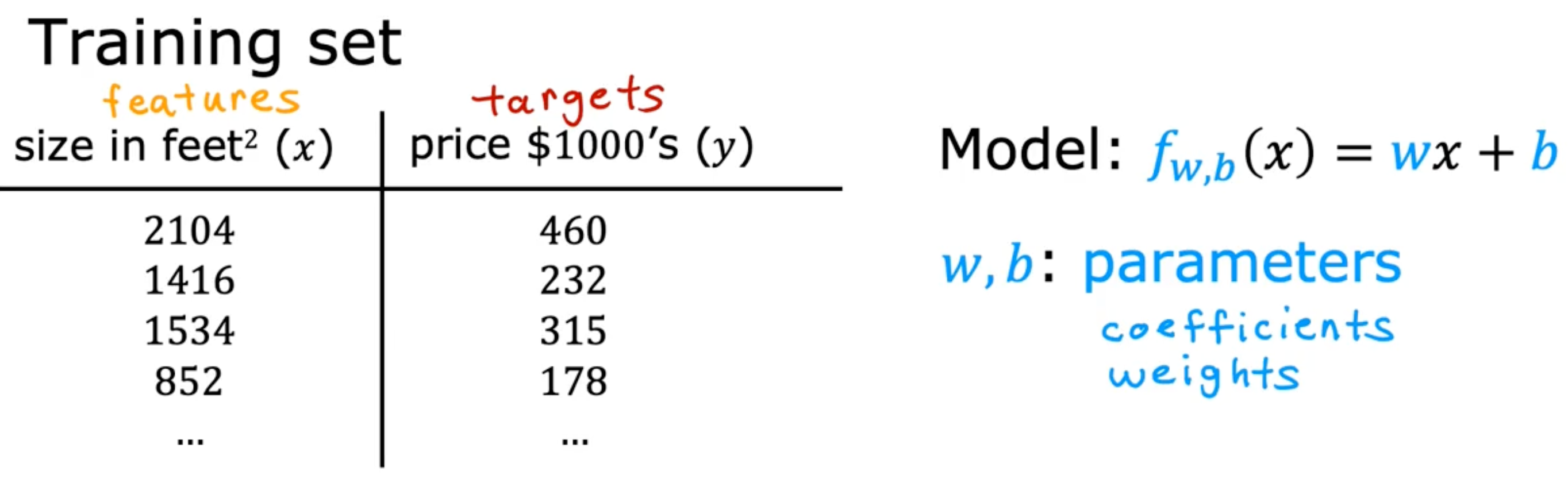
Linear Regression Model
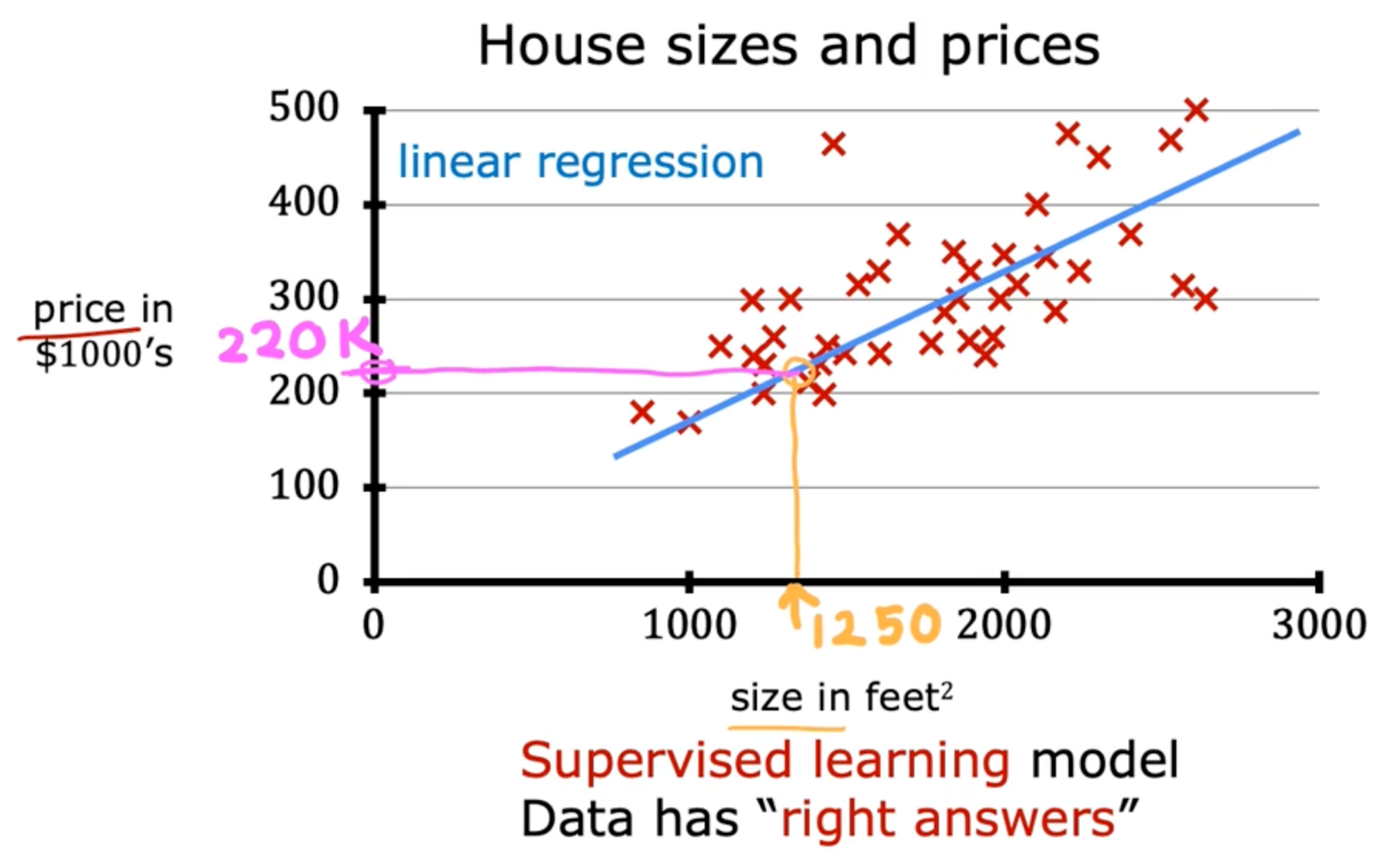
Terminology
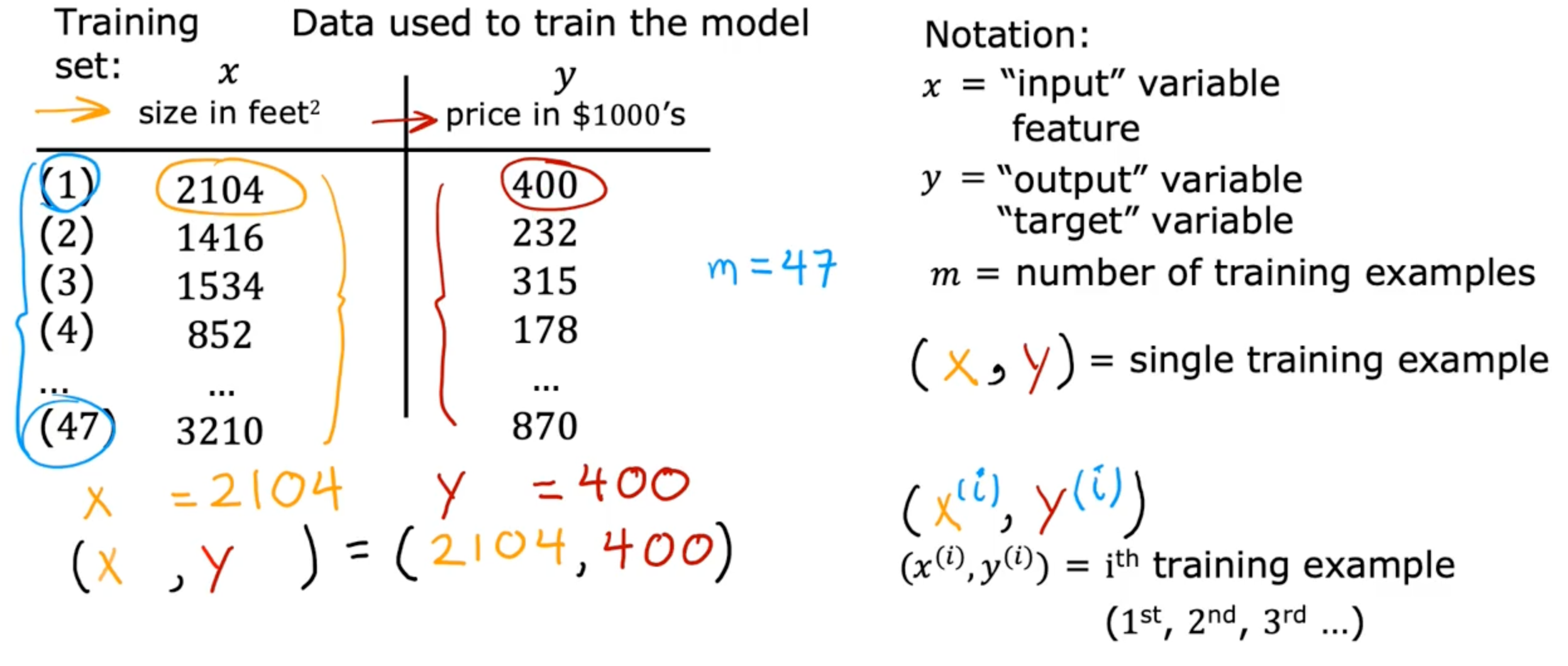
- Training set - data used to train the model
- x - input variable feature
- y - output variable, target variable
- m - number of training examples
- (x,y) - single training example
- (x(i),y(i)) - ith training example
- ex) (x(1),y(1))=(2104,400)
Cost Function
What do w, b do?
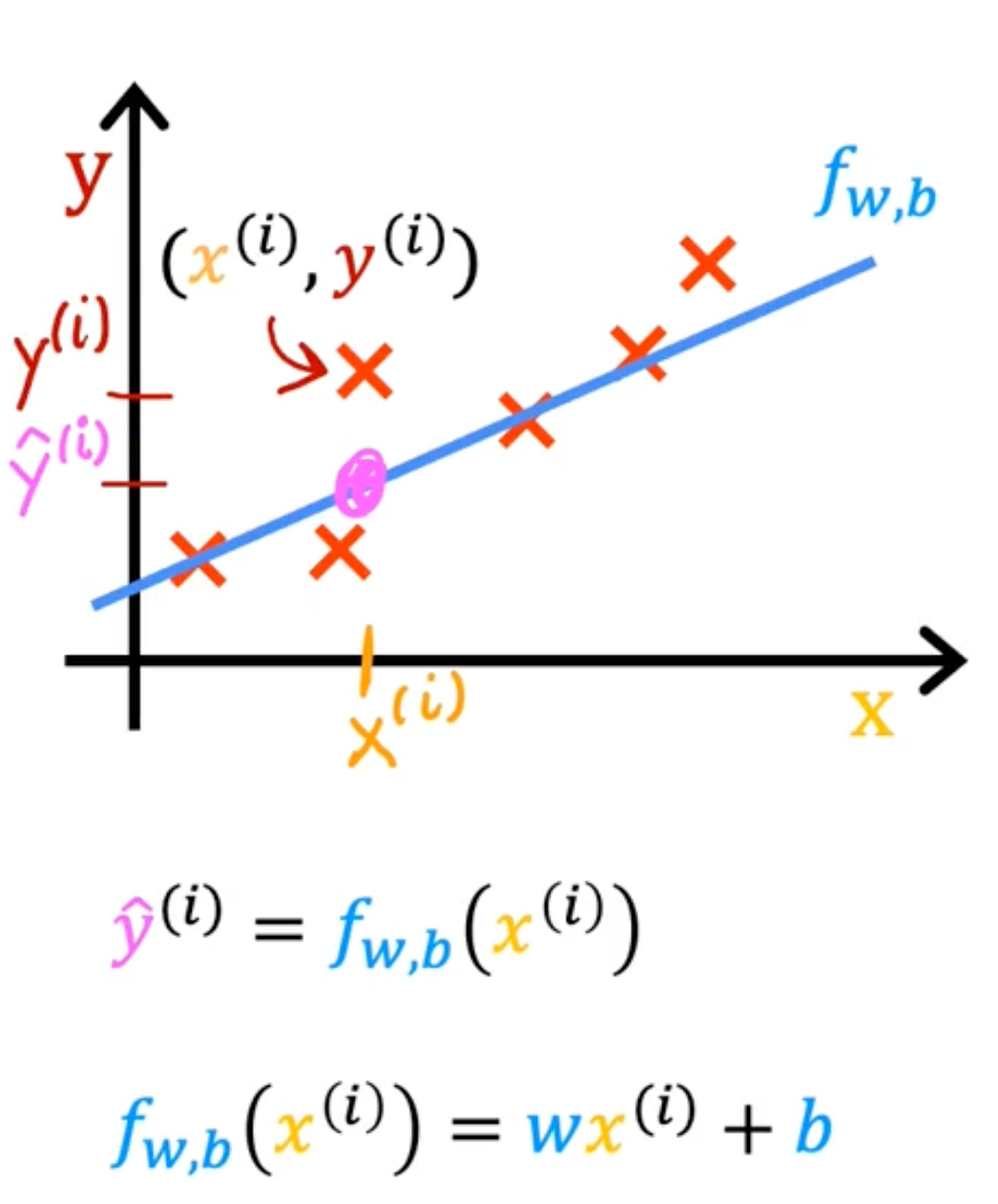
Find w,b:
y^(i) is close to y(i) for all (x(i),y(i))
Cost function
cost function is to see how well the model is doing
J(w,b)=2m1i=1∑m(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))2
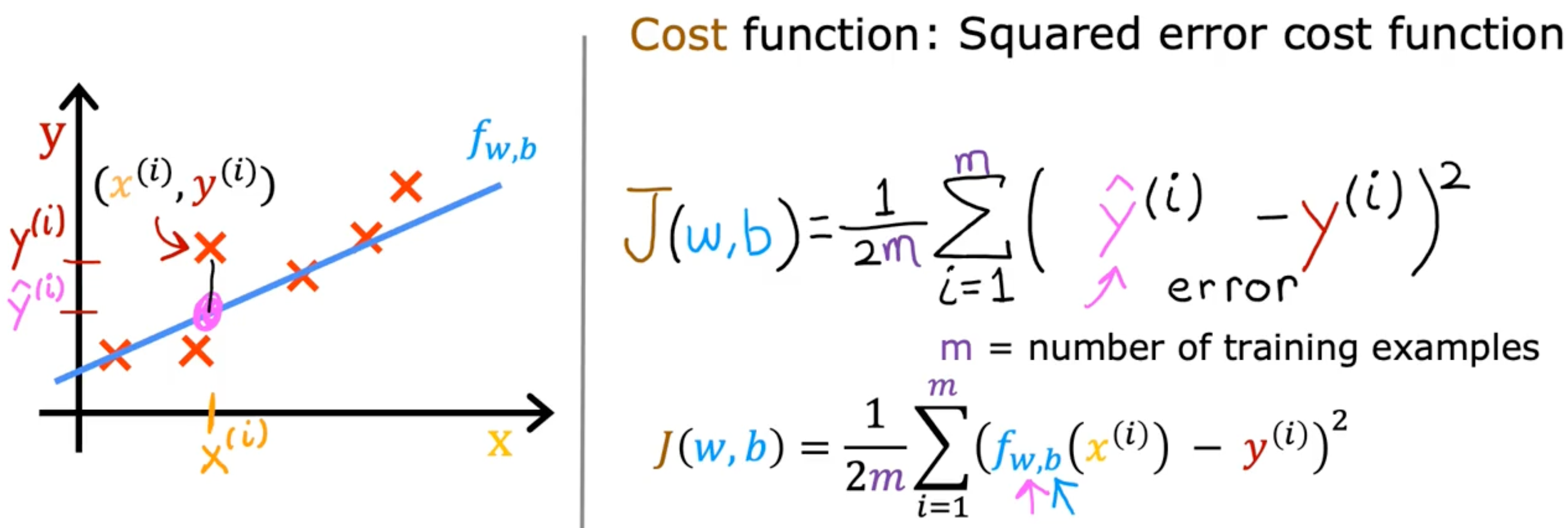
- error : y^(i)−y(i) (prediction_i - realvalue_i)
- different people use different cost function
- squared error cost function is the most commonly used one
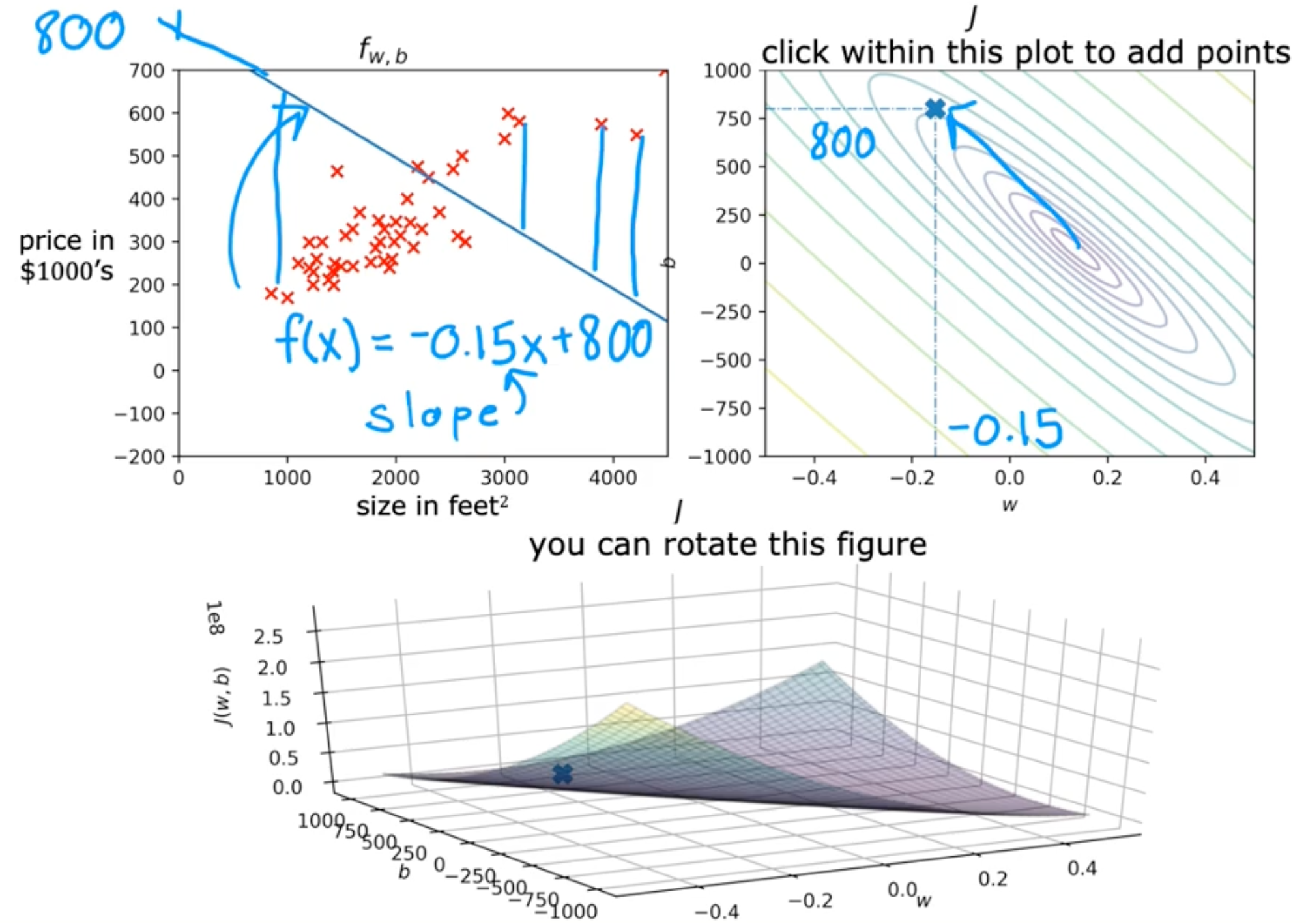
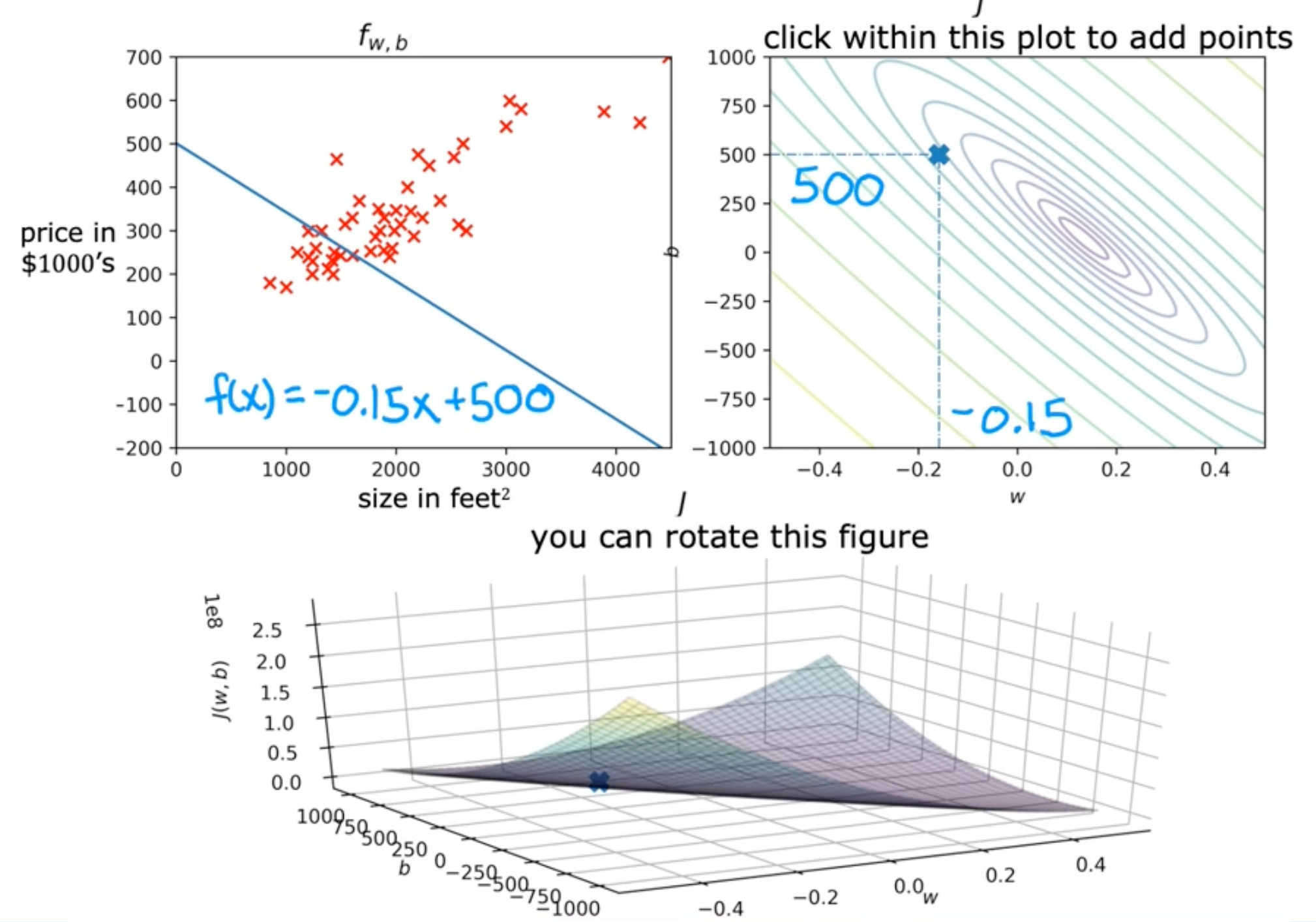
Cost function intuition
- model
- fw,b(x)=wx+b
- parameter
- cost function
- J(w,b)=2m1∑i=1m(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))2
- goal
- minimizew,bJ(w,b)
Simplified cost function
-
model
- fw(x)=wx
-
parameter
-
cost function
- J(w)=2m1∑i=1m(fw(x(i))−y(i))2
-
goal
- minimizewJ(w)
-
examples
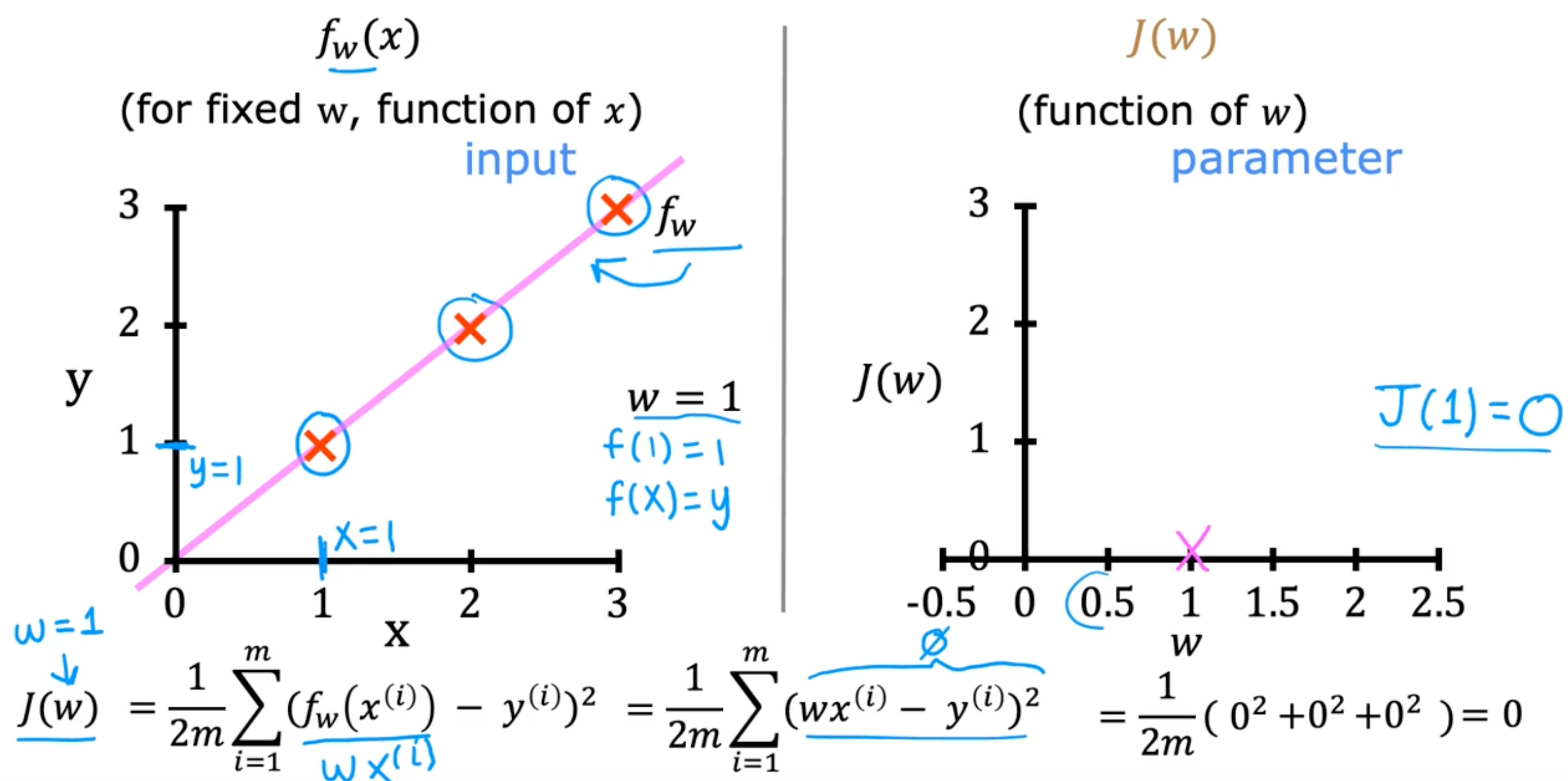
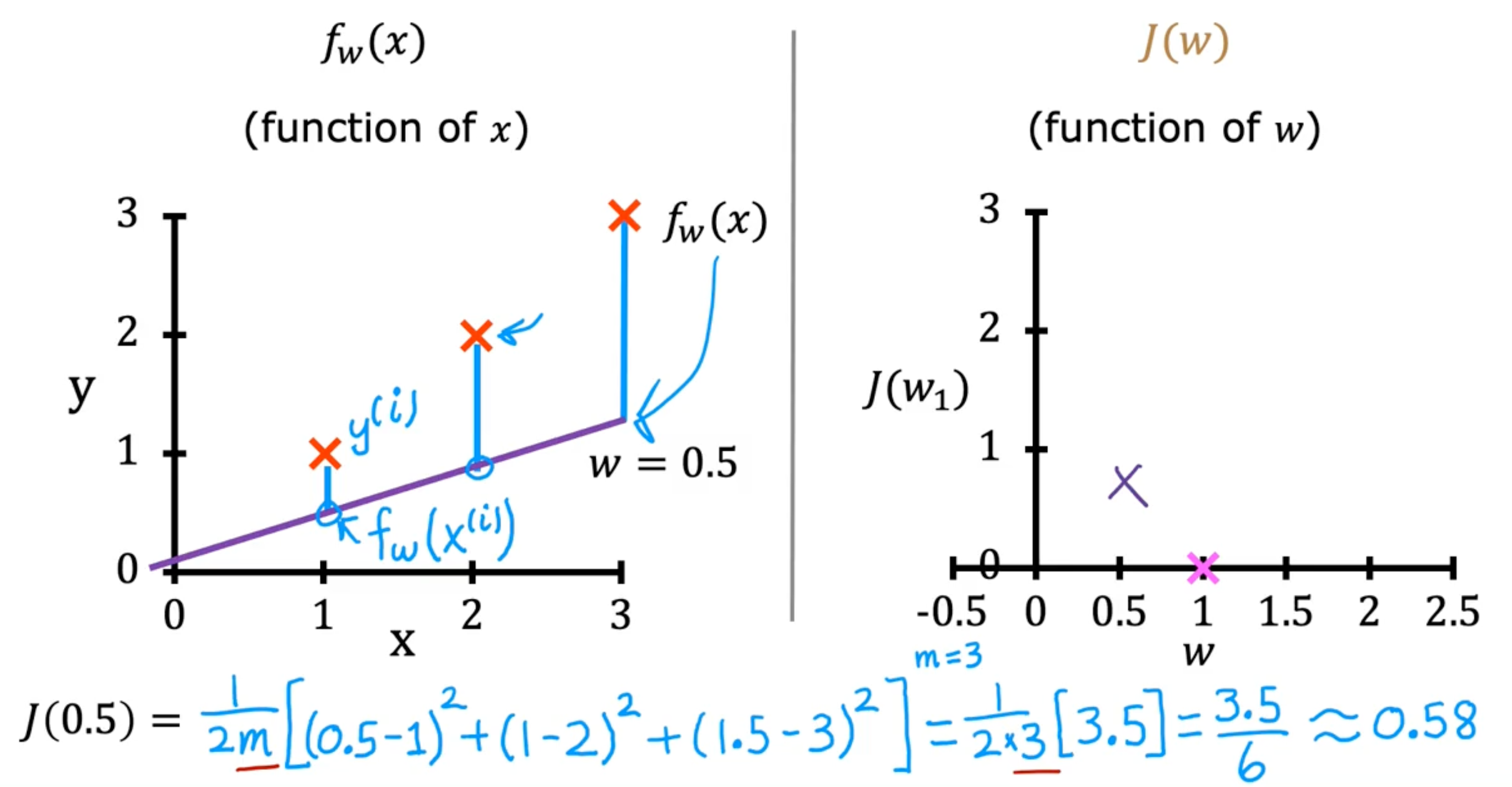
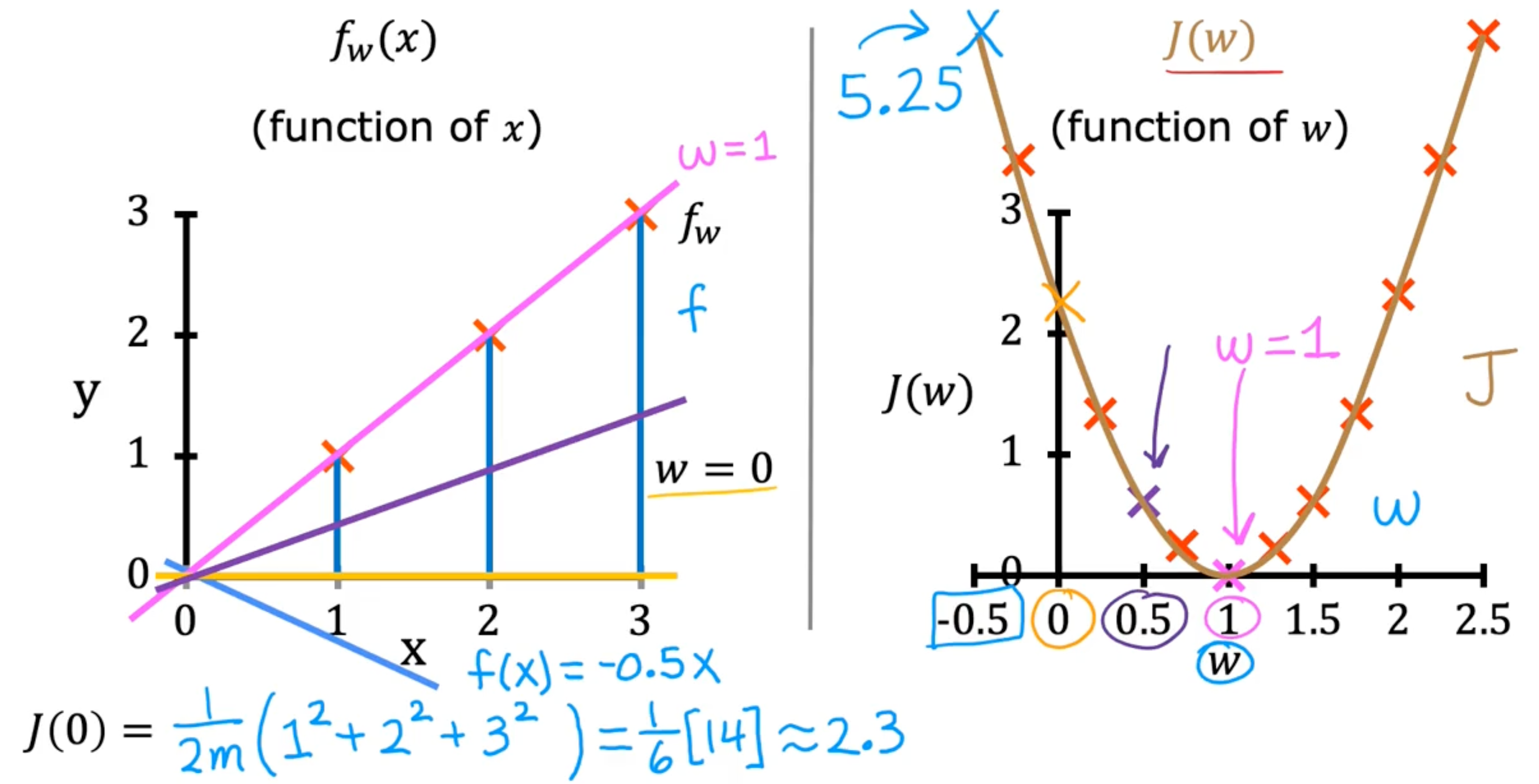
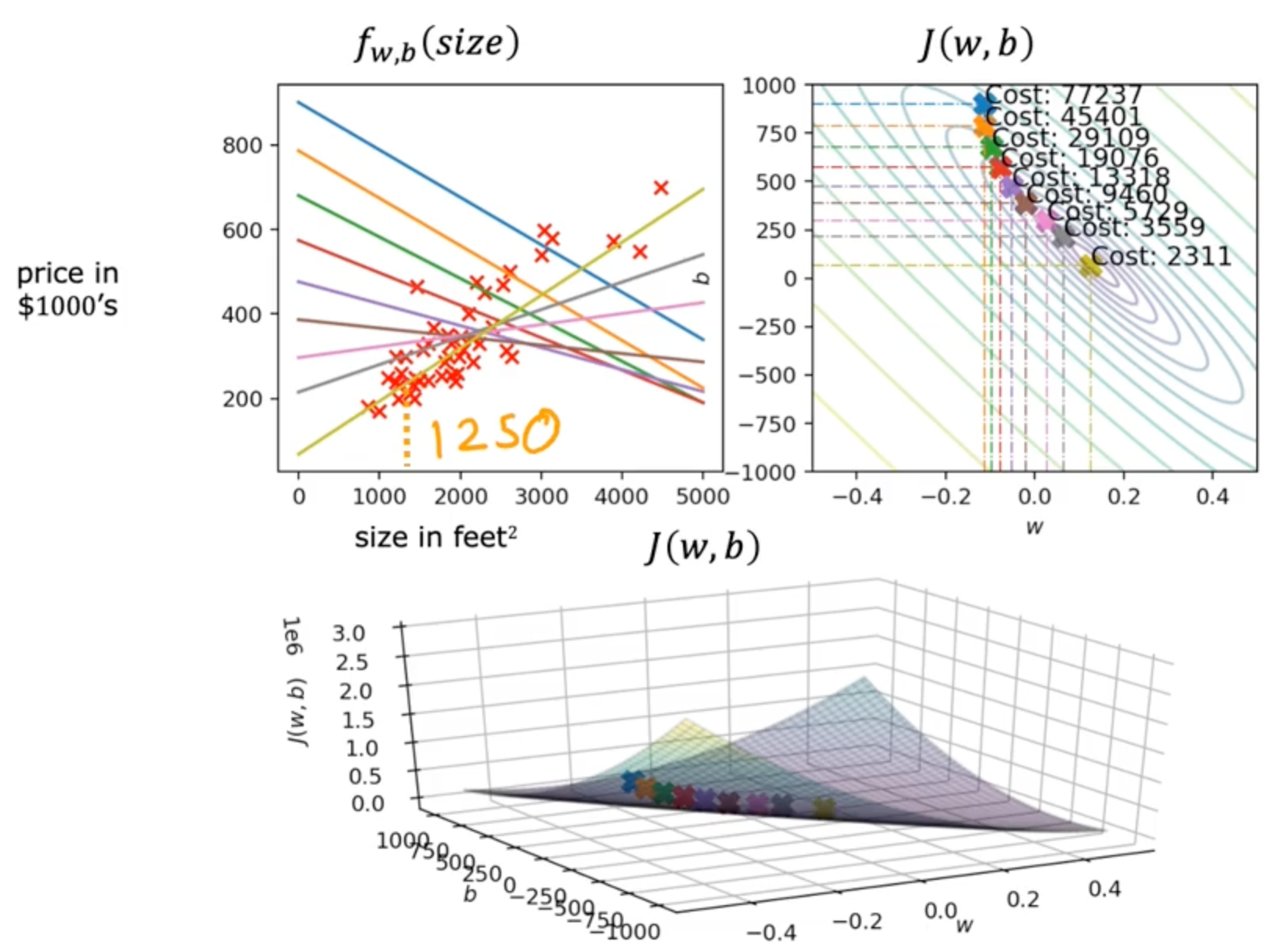
Visualizing the cost function
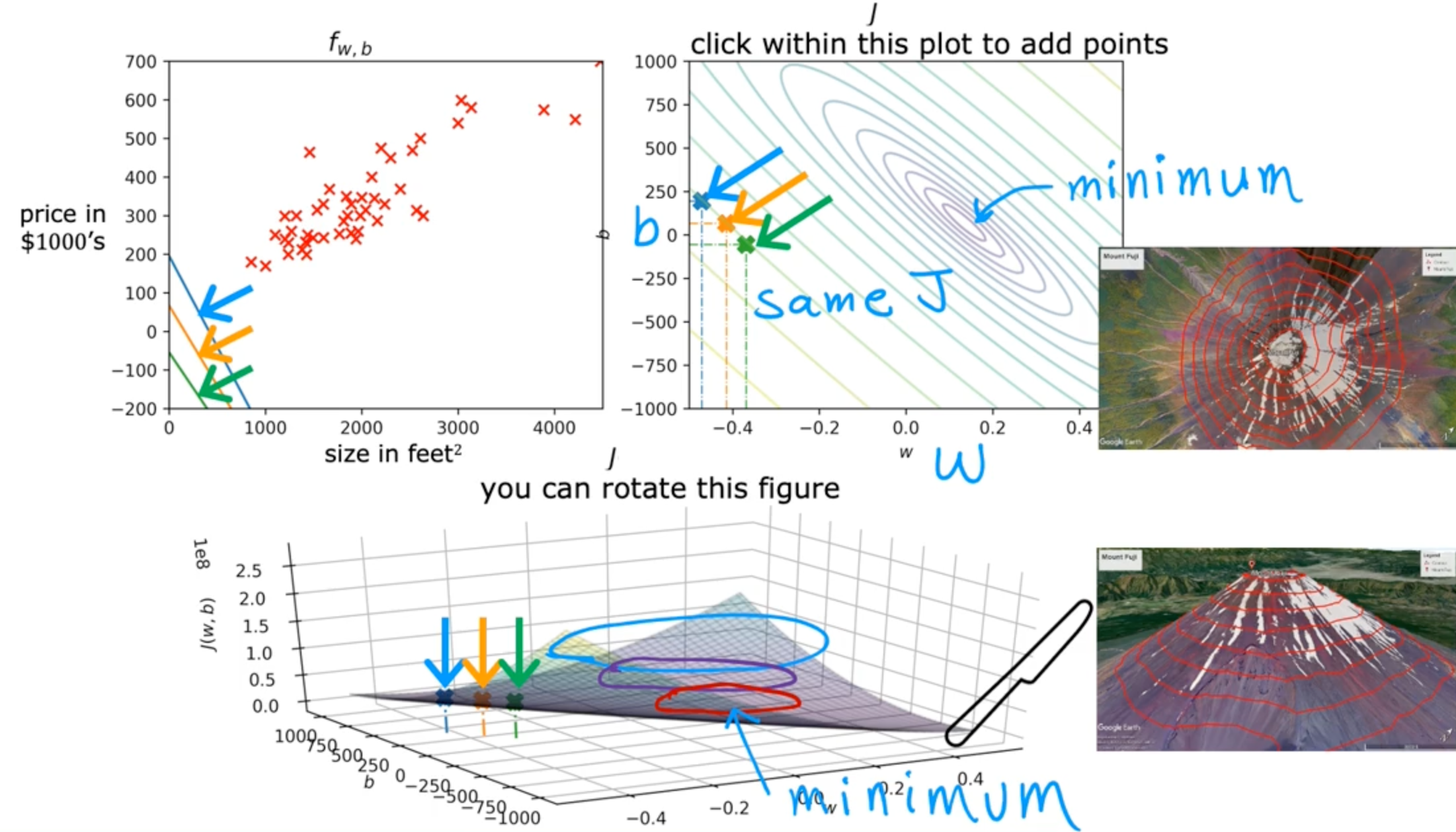
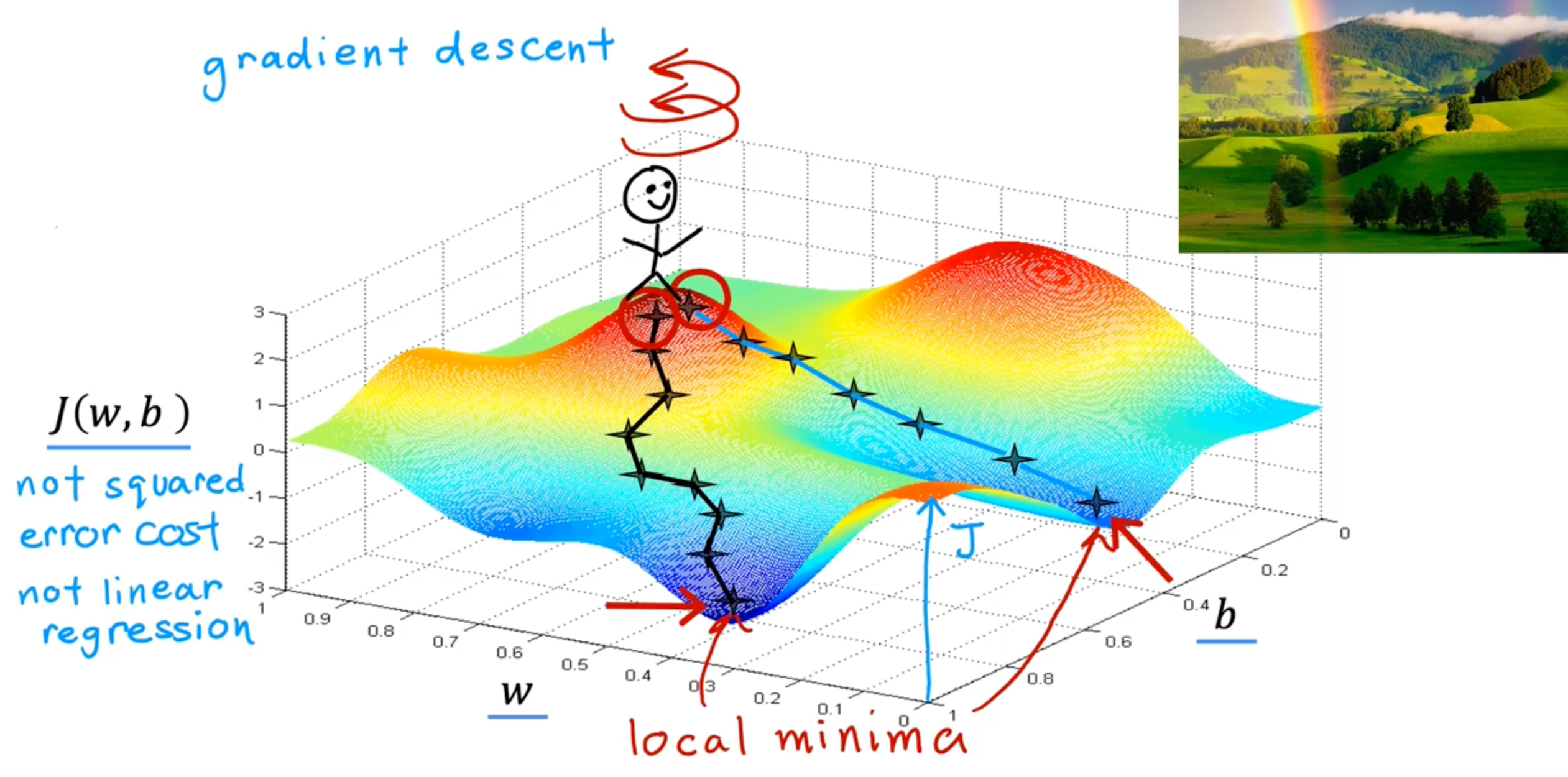
Gradient Descent
Have some function J(w,b) for linear regression or any function
Want minw,bJ(w,b)
Outline:
- Start with some w, b (set w=0,b=0)
- keep changing w,b to reduce J(w,b)
- until we settle at or near a minimum
-
may have > 1 minimum
Implementing gradient descent
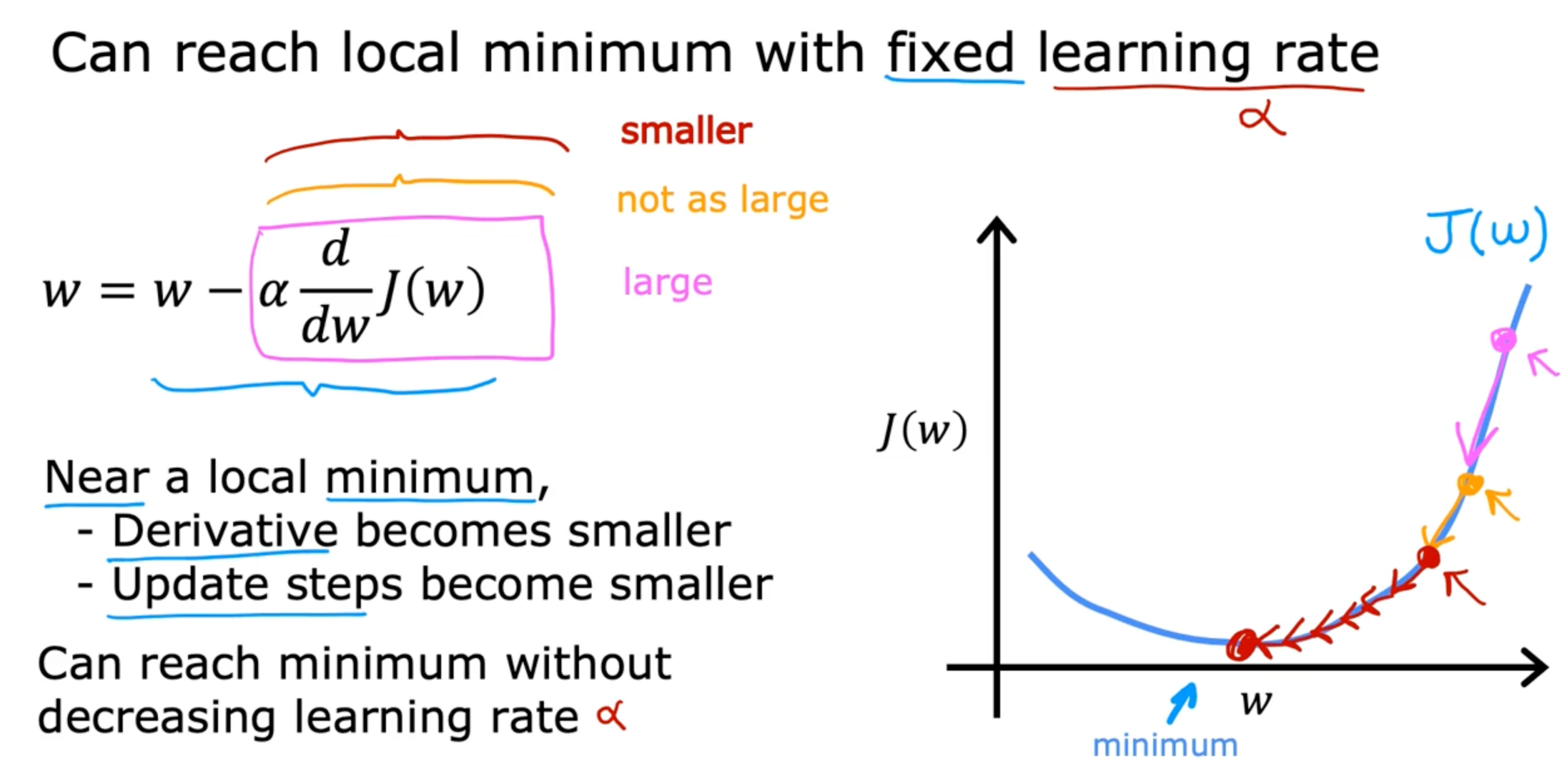
Gradient descent algorithm
simultaneously update w and b
w=w−adwdJ(w,b)
b=b−adbdJ(w,b)
a: learning rate
dwdJ(w,b): Derivative
Gradient descent intuition
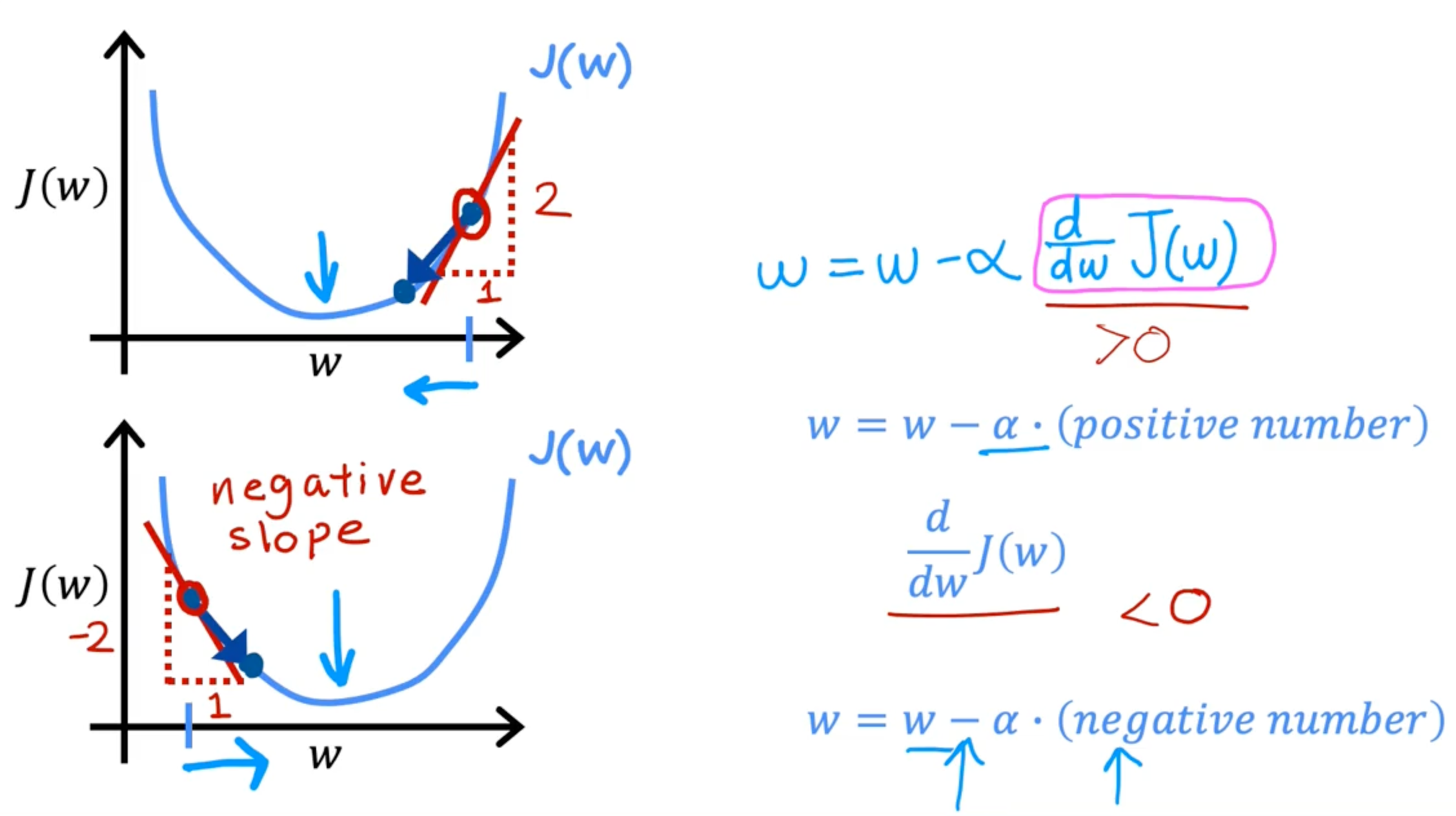
Learning rate
if a is too small, gradient descent may be slow
if a is too large, gradient descent may:
- overshoot, never reach minimum
- fail to converge, diverge
Gradient descent for linear regression
Linear regression model
fw,b(x)=wx+b
Cost function
J(w,b)=2m1i=1∑m(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))2
Gradient descent algorithm
repeat until convergence
w=w−adwdJ(w,b)
- w=w−adwdJ(w,b)
- m1∑i=1m(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))x(i)
b=b−adbdJ(w,b)
- b=b−adbdJ(w,b)
- m1∑i=1m(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))
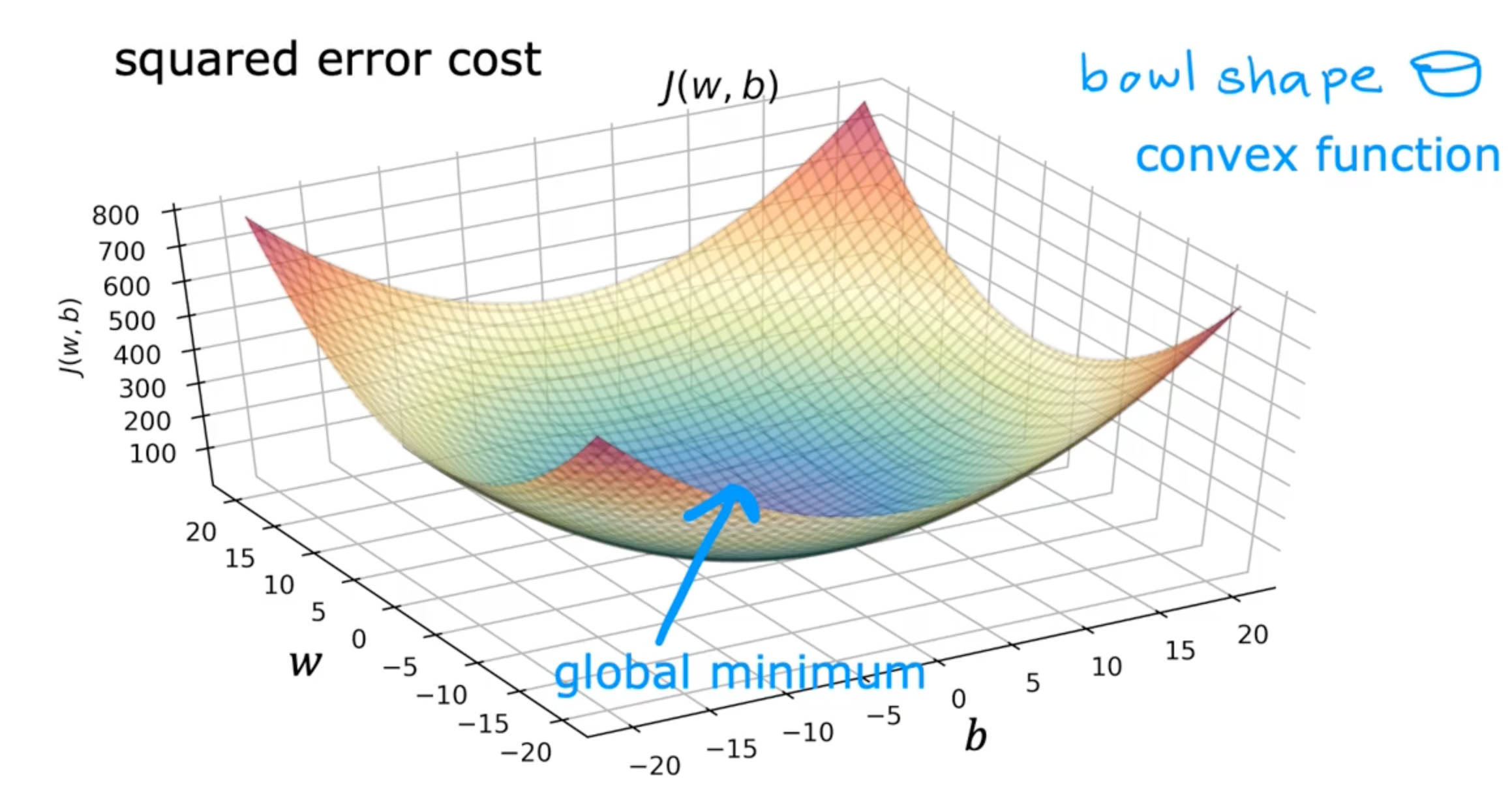
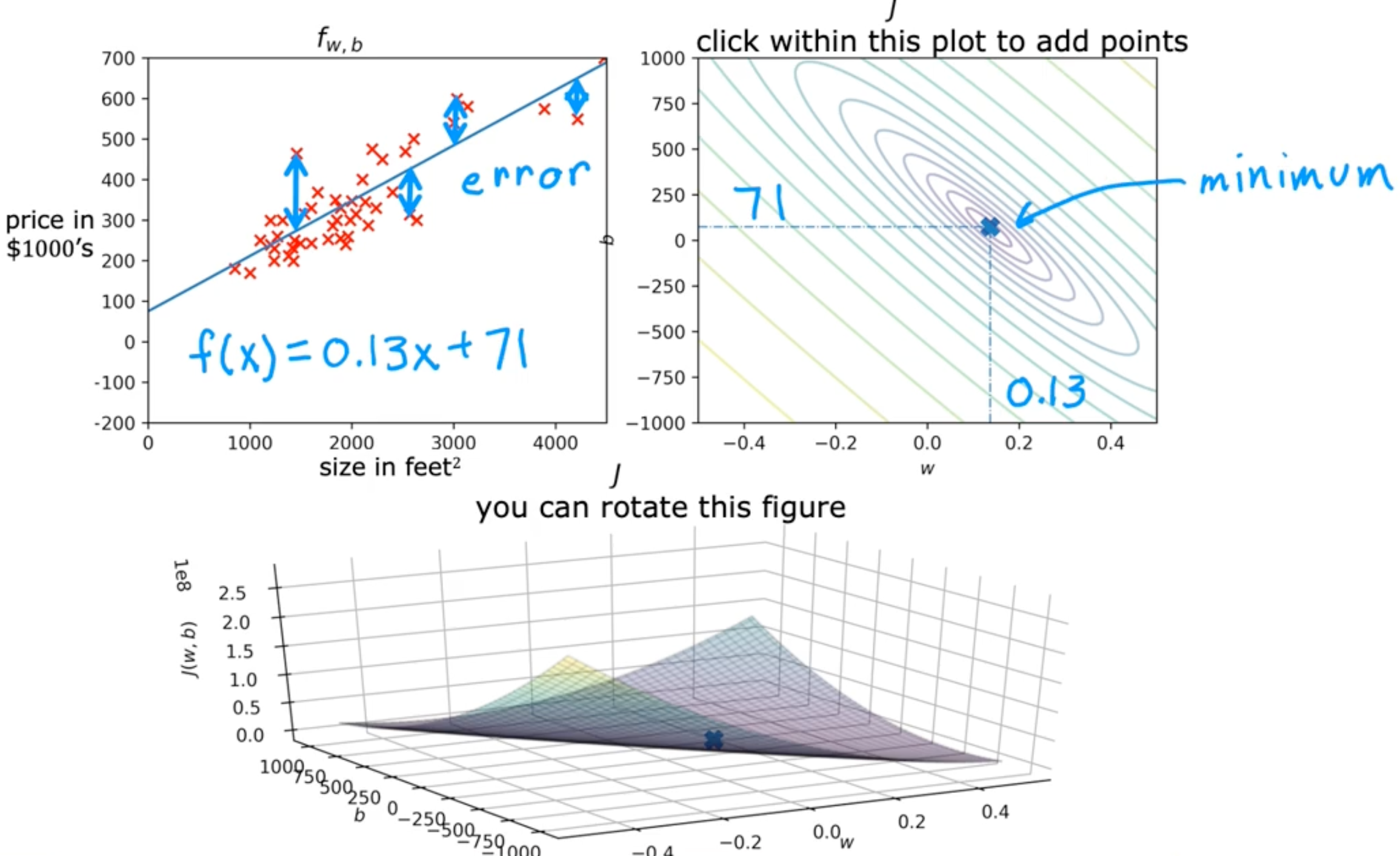
- squared error cost will never have local minimum
- gradient descent with convex function will always converge with global minimum
Mathematics
m1∑i=1m(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))x(i)
- dwdJ(w,b)
- dwd2m1∑i=1m(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))2
- dwd2m1∑i=1m(wx(i)+b−y(i))2
- 2m1∑i=1m(wx(i)+b−y(i))2x(i)
m1∑i=1m(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))
- dbdJ(w,b)
- dbd2m1∑i=1m(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))2
- dbd2m1∑i=1m(wx(i)+b−y(i))2
- 2m1∑i=1m(wx(i)+b−y(i))2
Running gradient descent
Source
Machine Learning